Starting a trade policy master’s dissertation is a fascinating but difficult task. One of the most important aspects of your research is empirical investigation from valid sources. It mainly involves gathering and evaluating actual data to bolster your claims and add more knowledge.
According to the World Trade Organisation, the amount of global merchandise trade is expected to increase by 1.7% in 2023 and 3.2% in 2024. In 2022, trade volume growth was 2.7%, lower than predicted after a weak fourth quarter.
We understand that students often face difficulties in researching and writing such dissertations. But with the help of this detailed and user-friendly roadmap, you’ll find it easy-going. However, if you are still unable to write it perfectly, you should get dissertation writing services from The Academic Papers UK.
Here, we will guide you about trade policy and lead you through the complexities of conducting empirical research for your trade policy master’s dissertation.
What is Trade Policy?
A government’s set of guidelines and rules governing its foreign trade operations is referred to as its trade policy. It describes the policies, goals, and limitations pertaining to the imports and exports of goods and services.
Its main intention is to foster economic expansion, safeguard homegrown businesses, and maintain equilibrium in international trade relations. In developing countries, trade policy directly impacts economic growth, promoting international trade and eliminating trade barriers.
In a research paper, Food problem and its solution, the following trade policy master’s dissertation example is explained to better understand trade policy.
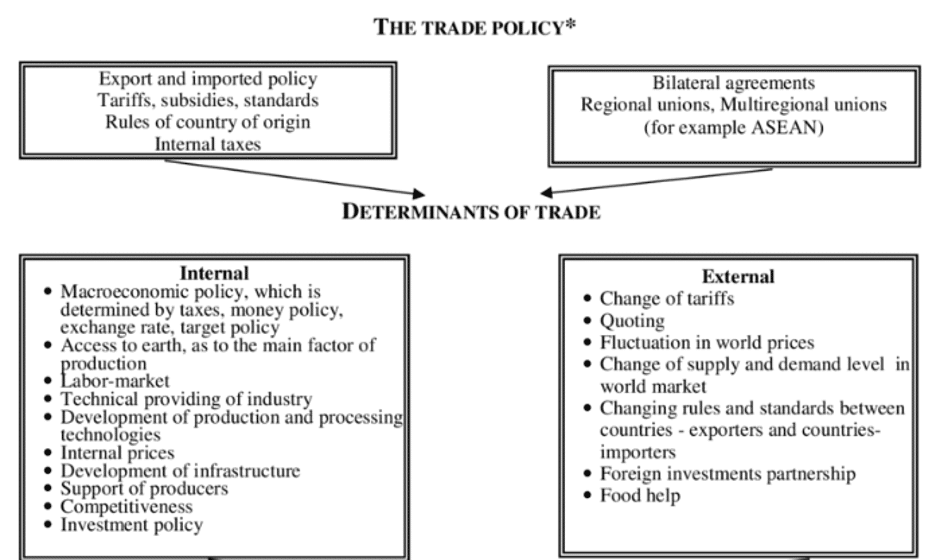
Step-by-Step Guide to Conduct Research for Trade Policy Master’s Dissertation
Step 1: Identify the Topic of Your Study
Clearly define your research question before you embark on your empirical research trip. Your inquiry has to be clear, pertinent, and in line with the goals of your dissertation on trade policy. Take into account the gaps in the body of knowledge and strive to make a significant contribution to the area.
Step 2: Choose Your Research Design
Your empirical study’s success depends on your choice of research design. In trade policy research, students mostly use cross-sectional, longitudinal, and experimental designs. Select the option that best aligns with your study question and available resources, as each offers advantages and disadvantages. Deeply go through each step and analyse your options before selecting a research design for your trade policy master dissertations.
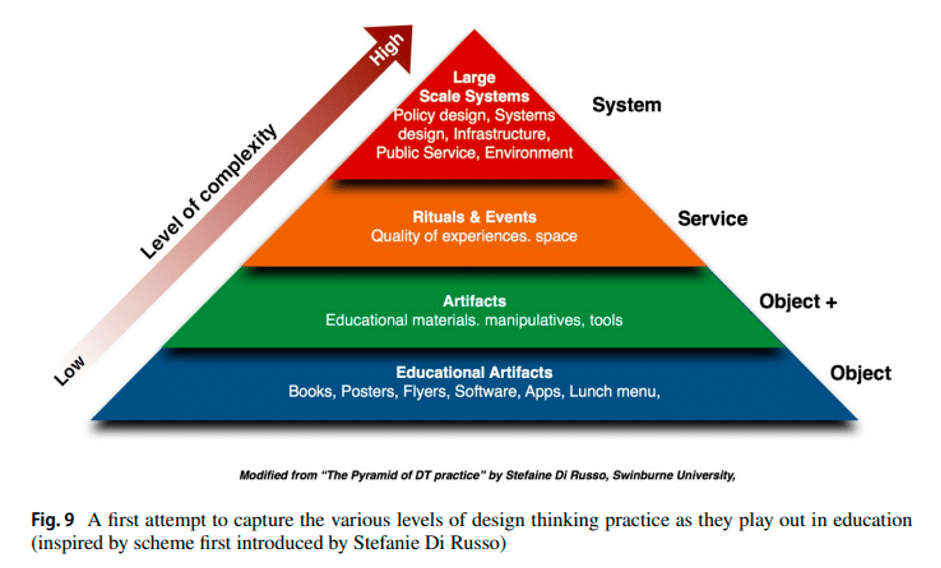
Step 3: Design a Theory
Develop a theory in response to your research topic. A tentative claim that implies a connection between variables is called a hypothesis. Make sure your hypothesis is relevant to your research aims, testable, and specific.
Follow the following pyramid steps to design your theory, taken from Designing Theory:
Step 4: Determine the Data Sources and Variables
Decide which variables are best appropriate for your research and clearly identify them. Government reports databases on international commerce, surveys, and interviews are a few examples of data sources for trade policy research. Make sure the sources you have picked are trustworthy and reputable.
Step 5: Data Collection
Put your preferred data collection techniques into practice while working on your trade policy master’s dissertation. Information extraction from pre-existing databases, content analysis, surveys, and interviews may all be used in this process. To guarantee the dependability and correctness of your facts, exercise caution in your method.
Step 6: Analyzing Data
It’s time to assess your data after you’ve gathered it. You may employ statistical techniques, qualitative analysis, or a combination of the two, depending on the type of data you have. Factor analysis, econometric modelling, and regression analysis are frequently used statistical techniques in trade policy research.
Step 7: Results Interpretation
Analyse your results in light of your hypothesis and research question of trade policy master’s dissertations. Talk about how your findings affect trade policy and how they add to the existing corpus of information. Adding visuals like images, graphs, and charts can also enhance your interpretation of results.
Step 8: Conclusion and Recommendations
List the main conclusions you came to and reiterate their importance. Provide recommendations to improve the trade policy and practices. Portray your research results in the conclusion as you wrap up your empirical study.
Step 9: Writing Your Dissertation
Your dissertation should have an organised structure with an introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Explain your research methodology, conclusions, and ramifications in plain language. Keep in mind that your dissertation writing should be in accordance with the accepted academic standards.
Trade Policy Master’s Dissertation Structure
You can find the dissertation structure from various books online, including The Dissertation Journey. Generally, a master’s dissertation on trade policy has the following format:
- Introduction: Presents the topic, the research question, and the hypothesis. It also sets the scene for the study.
- Literature review: Identifies gaps in knowledge and establishes a theoretical framework for the study. Review the prior research and literature on the selected trade policy topic.
- Methodology: Explain the approach that you would take to answer the research question or test the hypothesis. It includes the study design, data-gathering strategies, and analytic procedures.
- Results: Outlines the empirical research’s conclusions, frequently with the help of tables, charts, or graphs to show the information.
- Discussion: Examine the findings in light of the study topic, connect them to the body of literature already in existence, and talk about how trade policy may be affected.
- Conclusion: Provides a synopsis of the most important findings. Moreover, restates the value of the research and makes some suggestions for additional research.
- References: Provides an inventory of all the sources cited in the dissertation, adhering to a particular citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago).
- Appendices: It contains extra information that complements the main body of the dissertation. It may include survey instruments, raw data, or other supporting resources.
Conclusion
Carrying out an empirical study for your trade policy master’s dissertation is a demanding yet worthwhile project. By following these guidelines, you can successfully negotiate the challenges of the research process and offer insightful contributions to the field. You must follow a proper dissertation structure to produce a well-written dissertation demonstrating your trade policy proficiency.
Don’t you have enough time to do thorough research and writing, or do you have no skills to do it perfectly? Are you looking for expert help? In this scenario, we advise you to buy a trade policy master’s dissertation from English writers of The Academic Papers UK. They are expert in trade policy research and writing and offer 24/7 dissertation writing services online.


